
- FUNDAMENTAL THEOREM OF CALCULUS CALCULATOR HOW TO
- FUNDAMENTAL THEOREM OF CALCULUS CALCULATOR DOWNLOAD
Then the area under the graph correspond to total distance travelled by the car. The Second Fundamental Theorem of Calculus is the formal, more general statement of the preceding fact: if f is a continuous function and c is any constant, then A(x) xcf(t)dt is the unique antiderivative of f that satisfies A(c) 0.
FUNDAMENTAL THEOREM OF CALCULUS CALCULATOR DOWNLOAD
This also works when $y$ axis is the speed of a moving object instead of a download speed.įor example, if you graph the speed of a moving car, with kilometres per hour on the $y$ axis, This is one reason why integrals are interesting: they allow representing real-world things as areas. What we will use most from FTC 1 is that. is continuous on a, b, differentiable on ( a, b), and g ( x) f ( x).
FUNDAMENTAL THEOREM OF CALCULUS CALCULATOR HOW TO
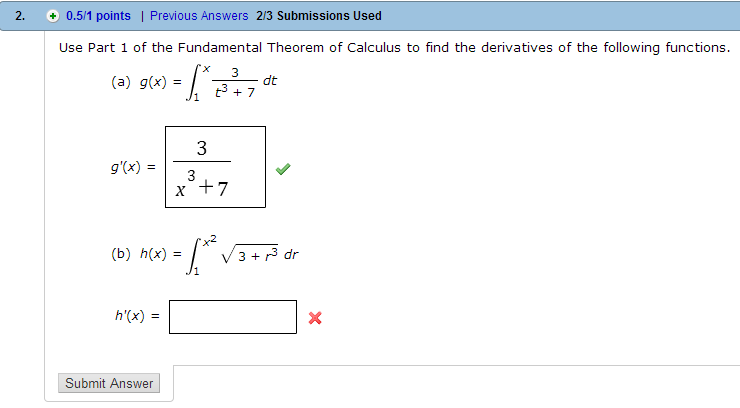
We have $I'(t) = t^2$ for all numbers $t$. Learn how to perform specific operations and calculations related to the fundamental theorem of calculus on the TI-84 Plus CE graphing calculator.For the ful. Fundamental Theorem of Calculus (Part 1) If f is a continuous function on a, b, then the integral function g defined by. (I'm using $t$ instead of $b$ because I want to use the letter $b$ for a different thing later.)īecause $x^2$ is continuous, by part 1 of the fundamental theorem of calculus, The first part of the theorem says that if we first integrate and then differentiate the result. The fundamental theorem establishes the link between the two. These two concepts apparently seem to have no relation between them, one arises from an area problem and the other from a tangent problem. If f happens to be a positive function, then g (x) can be interpreted as the area under the graph of f from a to x. The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus states the relationship between differentiation and integration of a function. Let f(x) be a continuous function (so, the denite integral of f(x) exists). Part 1 (FTC1) If f is a continuous function on a, b, then the function g defined by.

Defining determinants Permutations and transpositions Calculating determinants with row operations Determinant of transpose Determinant and matrix multiplication Fundamental Theorem of Calculus, Part 2 ¶ assertion of Fundamental Theorem of Calculus.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
